Action Function
Action functions allow you to write custom buttons that appear in the message toolbar for end users to interact with. This feature enables more interactive messaging, allowing users to grant permission before a task is performed, generate visualizations of structured data, download an audio snippet of chats, and many other use cases.
Action functions should always be defined as async. The backend is progressively moving toward fully async execution, and synchronous functions may block execution or cause issues in future releases.
Actions are admin-managed functions that extend the chat interface with custom interactive capabilities. When a message is generated by a model that has actions configured, these actions appear as clickable buttons beneath the message.
A scaffold of Action code can be found in the community section. For more Action Function examples built by the community, visit https://openwebui.com/search.
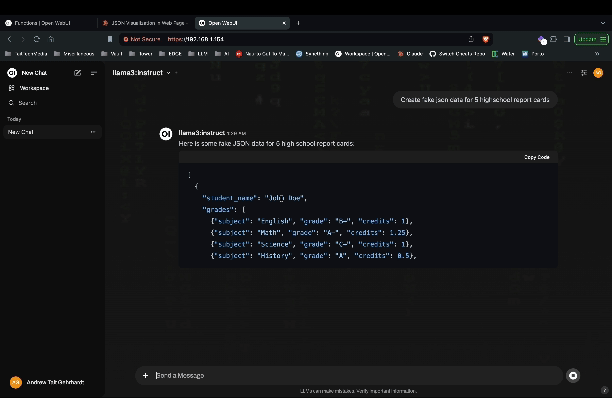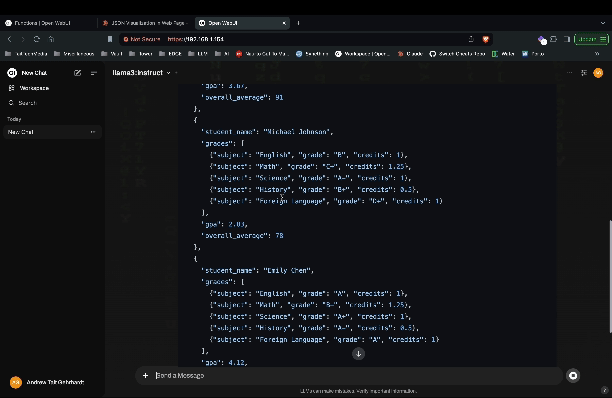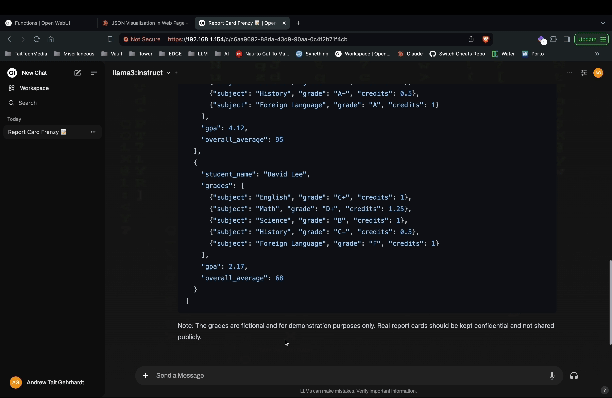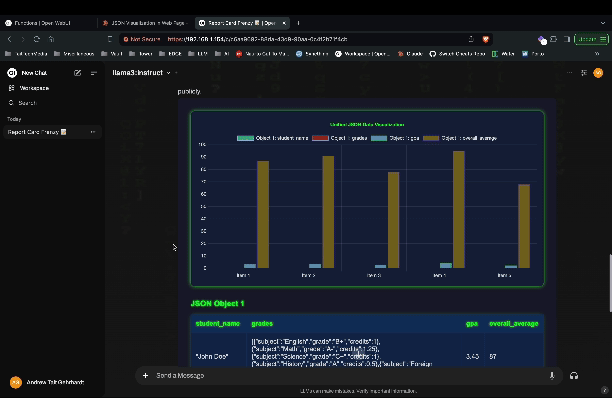
An example of a graph visualization Action can be seen in the video below.
Action Function Architecture
Actions are Python-based functions that integrate directly into the chat message toolbar. They execute server-side and can interact with users through real-time events, modify message content, and access the full Open WebUI context.
Function Structure
Actions follow a specific class structure with an action method as the main entry point:
class Action:
def __init__(self):
self.valves = self.Valves()
class Valves(BaseModel):
# Configuration parameters
parameter_name: str = "default_value"
async def action(self, body: dict, __user__=None, __event_emitter__=None, __event_call__=None):
# Action implementation
return {"content": "Modified message content"}
Action Method Parameters
The action method receives several parameters that provide access to the execution context:
body- Dictionary containing the message data and context__user__- Current user object with permissions and settings__event_emitter__- Function to send real-time updates to the frontend__event_call__- Function for bidirectional communication (confirmations, inputs)__model__- Model information that triggered the action__request__- FastAPI request object for accessing headers, etc.__id__- Action ID (useful for multi-action functions)
Event System Integration
Actions can utilize Open WebUI's real-time event system for interactive experiences:
Event Emitter (__event_emitter__)
For more information about Events and Event emitters, see Events and Event Emitters.
Send real-time updates to the frontend during action execution:
async def action(self, body: dict, __event_emitter__=None):
# Send status updates
await __event_emitter__({
"type": "status",
"data": {"description": "Processing request..."}
})
# Send notifications
await __event_emitter__({
"type": "notification",
"data": {"type": "info", "content": "Action completed successfully"}
})
Event Call (__event_call__)
Request user input or confirmation during execution:
async def action(self, body: dict, __event_call__=None):
# Request user confirmation
response = await __event_call__({
"type": "confirmation",
"data": {
"title": "Confirm Action",
"message": "Are you sure you want to proceed?"
}
})
# Request user input
user_input = await __event_call__({
"type": "input",
"data": {
"title": "Enter Value",
"message": "Please provide additional information:",
"placeholder": "Type your input here..."
}
})
Action Types and Configurations
Single Actions
Standard actions with one action method:
async def action(self, body: dict, **kwargs):
# Single action implementation
return {"content": "Action result"}
Multi-Actions
Functions can define multiple sub-actions through an actions array:
actions = [
{
"id": "summarize",
"name": "Summarize",
"icon_url": "data:image/svg+xml;base64,..."
},
{
"id": "translate",
"name": "Translate",
"icon_url": "data:image/svg+xml;base64,..."
}
]
async def action(self, body: dict, __id__=None, **kwargs):
if __id__ == "summarize":
# Summarization logic
return {"content": "Summary: ..."}
elif __id__ == "translate":
# Translation logic
return {"content": "Translation: ..."}
Global vs Model-Specific Actions
- Global Actions - Turn on the toggle in the Action's settings, to globally enable it for all users and all models.
- Model-Specific Actions - Configure enabled actions for specific models in the model settings.
Advanced Capabilities
Background Task Execution
For long-running operations, actions can integrate with the task system:
async def action(self, body: dict, __event_emitter__=None):
# Start long-running process
await __event_emitter__({
"type": "status",
"data": {"description": "Starting background processing..."}
})
# Perform time-consuming operation
result = await some_long_running_function()
return {"content": f"Processing completed: {result}"}
File and Media Handling
Actions can work with uploaded files and generate new media:
async def action(self, body: dict):
message = body
# Access uploaded files
if message.get("files"):
for file in message["files"]:
# Process file based on type
if file["type"] == "image":
# Image processing logic
pass
# Return new files
return {
"content": "Analysis complete",
"files": [
{
"type": "image",
"url": "generated_chart.png",
"name": "Analysis Chart"
}
]
}
User Context and Permissions
Actions can access user information and respect permissions:
async def action(self, body: dict, __user__=None):
if __user__["role"] != "admin":
return {"content": "This action requires admin privileges"}
user_name = __user__["name"]
return {"content": f"Hello {user_name}, admin action completed"}
Example - Specifying Action Frontmatter
Each Action function can include a docstring at the top to define metadata for the button. This helps customize the display and behavior of your Action in Open WebUI.
Example of supported frontmatter fields:
title: Display name of the Action.author: Name of the creator.version: Version number of the Action.required_open_webui_version: Minimum compatible version of Open WebUI.icon_url (optional): URL or Base64 string for a custom icon.
Base64-Encoded Example:
Example
"""
title: Enhanced Message Processor
author: @admin
version: 1.2.0
required_open_webui_version: 0.5.0
icon_url: data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB3aWR0aD0iMjQiIGhlaWdodD0iMjQiIHZpZXdCb3g9IjAgMCAyNCAyNCIgZmlsbD0ibm9uZSIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIj4KPHBhdGggZD0iTTEyIDJMMTMuMDkgOC4yNkwyMCA5TDEzLjA5IDE1Ljc0TDEyIDIyTDEwLjkxIDE1Ljc0TDQgOUwxMC45MSA4LjI2TDEyIDJaIiBzdHJva2U9ImN1cnJlbnRDb2xvciIgc3Ryb2tlLXdpZHRoPSIyIiBzdHJva2UtbGluZWNhcD0icm91bmQiIHN0cm9rZS1saW5lam9pbj0icm91bmQiLz4KPHN2Zz4K
requirements: requests,beautifulsoup4
"""
from pydantic import BaseModel
class Action:
def __init__(self):
self.valves = self.Valves()
class Valves(BaseModel):
api_key: str = ""
processing_mode: str = "standard"
async def action(
self,
body: dict,
__user__=None,
__event_emitter__=None,
__event_call__=None,
):
# Send initial status
await __event_emitter__({
"type": "status",
"data": {"description": "Processing message..."}
})
# Get user confirmation
response = await __event_call__({
"type": "confirmation",
"data": {
"title": "Process Message",
"message": "Do you want to enhance this message?"
}
})
if not response:
return {"content": "Action cancelled by user"}
# Process the message
original_content = body.get("content", "")
enhanced_content = f"Enhanced: {original_content}"
return {"content": enhanced_content}
Best Practices
Error Handling
Always implement proper error handling in your actions:
async def action(self, body: dict, __event_emitter__=None):
try:
# Action logic here
result = perform_operation()
return {"content": f"Success: {result}"}
except Exception as e:
await __event_emitter__({
"type": "notification",
"data": {"type": "error", "content": f"Action failed: {str(e)}"}
})
return {"content": "Action encountered an error"}
Performance Considerations
- Use async/await for I/O operations
- Implement timeouts for external API calls
- Provide progress updates for long-running operations
- Consider using background tasks for heavy processing
User Experience
- Always provide clear feedback through event emitters
- Use confirmation dialogs for destructive actions
- Include helpful error messages
Integration with Open WebUI Features
Actions integrate seamlessly with other Open WebUI features:
- Models - Actions can be model-specific or global
- Tools - Actions can invoke external tools and APIs
- Files - Actions can process uploaded files and generate new ones
- Memory - Actions can access conversation history and context
- Permissions - Actions respect user roles and access controls
For more examples and community-contributed actions, visit https://openwebui.com/search where you can discover, download, and explore custom functions built by the Open WebUI community.