SearXNG
This tutorial is a community contribution and is not supported by the Open WebUI team. It serves only as a demonstration on how to customize Open WebUI for your specific use case. Want to contribute? Check out the contributing tutorial.
This guide provides instructions on how to set up web search capabilities in Open WebUI using SearXNG in Docker.
SearXNG (Docker)
"SearXNG is a free internet metasearch engine which aggregates results from various search services and databases. Users are neither tracked nor profiled."
1. SearXNG Configuration
To configure SearXNG optimally for use with Open WebUI, follow these steps:
Step 1: git clone SearXNG Docker and navigate to the folder:
- Create a New Directory
searxng-docker
Clone the searxng-docker repository. This folder will contain your SearXNG configuration files. Refer to the SearXNG documentation for configuration instructions.
git clone https://github.com/searxng/searxng-docker.git
Navigate to the searxng-docker repository:
cd searxng-docker
Step 2: Locate and and modify the .env file:
- Uncomment
SEARXNG_HOSTNAMEfrom the.envfile and set it accordingly:
# By default listen on https://localhost
# To change this:
# * uncomment SEARXNG_HOSTNAME, and replace <host> by the SearXNG hostname
# * uncomment LETSENCRYPT_EMAIL, and replace <email> by your email (require to create a Let's Encrypt certificate)
SEARXNG_HOSTNAME=localhost:8080/
# LETSENCRYPT_EMAIL=<email>
# Optional:
# If you run a very small or a very large instance, you might want to change the amount of used uwsgi workers and threads per worker
# More workers (= processes) means that more search requests can be handled at the same time, but it also causes more resource usage
# SEARXNG_UWSGI_WORKERS=4
# SEARXNG_UWSGI_THREADS=4
Step 3: Modify the docker-compose.yaml file
- Remove the
localhostrestriction by modifying thedocker-compose.yamlfile:
sed -i "s/127.0.0.1:8080/0.0.0.0:8080/"
Step 4: Grant Necessary Permissions
- Allow the container to create new config files by running the following command in the root directory:
sudo chmod a+rwx searxng-docker/searxng
Step 5: Create a Non-Restrictive limiter.toml File
- Create a non-restrictive
searxng-docker/searxng/limiter.tomlconfig file:
searxng-docker/searxng/limiter.toml
# This configuration file updates the default configuration file
# See https://github.com/searxng/searxng/blob/master/searx/botdetection/limiter.toml
[botdetection.ip_limit]
# activate link_token method in the ip_limit method
link_token = false
[botdetection.ip_lists]
block_ip = []
pass_ip = []
Step 6: Remove the Default settings.yml File
- Delete the default
searxng-docker/searxng/settings.ymlfile if it exists, as it will be regenerated on the first launch of SearXNG:
rm searxng-docker/searxng/settings.yml
Step 7: Create a Fresh settings.yml File
On the first run, you must remove cap_drop: - ALL from the docker-compose.yaml file for the searxng service to successfully create /etc/searxng/uwsgi.ini. This is necessary because the cap_drop: - ALL directive removes all capabilities, including those required for the creation of the uwsgi.ini file. After the first run, you should re-add cap_drop: - ALL to the docker-compose.yaml file for security reasons.
- Bring up the container momentarily to generate a fresh settings.yml file:
docker compose up -d ; sleep 10 ; docker compose down
Step 8: Add Formats and Update Port Number
- Add HTML and JSON formats to the
searxng-docker/searxng/settings.ymlfile:
sed -i 's/formats: \[\"html\"\/]/formats: [\"html\", \"json\"]/' searxng-docker/searxng/settings.yml
Generate a secret key for your SearXNG instance:
sed -i "s|ultrasecretkey|$(openssl rand -hex 32)|g" searxng-docker/searxng/settings.yml
Windows users can use the following powershell script to generate the secret key:
$randomBytes = New-Object byte[] 32
(New-Object Security.Cryptography.RNGCryptoServiceProvider).GetBytes($randomBytes)
$secretKey = -join ($randomBytes | ForEach-Object { "{0:x2}" -f $_ })
(Get-Content searxng-docker/searxng/settings.yml) -replace 'ultrasecretkey', $secretKey | Set-Content searxng-docker/searxng/settings.yml
Update the port number in the server section to match the one you set earlier (in this case, 8080):
sed -i 's/port: 8080/port: 8080/' searxng-docker/searxng/settings.yml
Change the bind_address as desired:
sed -i 's/bind_address: "0.0.0.0"/bind_address: "127.0.0.1"/' searxng-docker/searxng/settings.yml
Configuration Files
searxng-docker/searxng/settings.yml (Extract)
The default settings.yml file contains many engine settings. Below is an extract of what the default settings.yml file might look like:
searxng-docker/searxng/settings.yml
# see https://docs.searxng.org/admin/settings/settings.html#settings-use-default-settings
use_default_settings: true
server:
# base_url is defined in the SEARXNG_BASE_URL environment variable, see .env and docker-compose.yml
secret_key: "ultrasecretkey" # change this!
limiter: true # can be disabled for a private instance
image_proxy: true
port: 8080
bind_address: "0.0.0.0"
ui:
static_use_hash: true
search:
safe_search: 0
autocomplete: ""
default_lang: ""
formats:
- html
- json # json is required
# remove format to deny access, use lower case.
# formats: [html, csv, json, rss]
redis:
# URL to connect redis database. Is overwritten by ${SEARXNG_REDIS_URL}.
# https://docs.searxng.org/admin/settings/settings_redis.html#settings-redis
url: redis://redis:6379/0
The port in the settings.yml file for SearXNG should match that of the port number in your docker-compose.yml file for SearXNG.
Step 9: Update uwsgi.ini File
- Ensure your
searxng-docker/searxng/uwsgi.inifile matches the following:
searxng-docker/searxng/uwsgi.ini
[uwsgi]
# Who will run the code
uid = searxng
gid = searxng
# Number of workers (usually CPU count)
# default value: %k (= number of CPU core, see Dockerfile)
workers = %k
# Number of threads per worker
# default value: 4 (see Dockerfile)
threads = 4
# The right granted on the created socket
chmod-socket = 666
# Plugin to use and interpreter config
single-interpreter = true
master = true
plugin = python3
lazy-apps = true
enable-threads = 4
# Module to import
module = searx.webapp
# Virtualenv and python path
pythonpath = /usr/local/searxng/
chdir = /usr/local/searxng/searx/
# automatically set processes name to something meaningful
auto-procname = true
# Disable request logging for privacy
disable-logging = true
log-5xx = true
# Set the max size of a request (request-body excluded)
buffer-size = 8192
# No keep alive
# See https://github.com/searx/searx-docker/issues/24
add-header = Connection: close
# uwsgi serves the static files
static-map = /static=/usr/local/searxng/searx/static
# expires set to one day
static-expires = /* 86400
static-gzip-all = True
offload-threads = 4
2. Alternative Setup
Alternatively, if you don't want to modify the default configuration, you can simply create an empty searxng-docker folder and follow the rest of the setup instructions.
Docker Compose Setup
Add the following environment variables to your Open WebUI docker-compose.yaml file:
services:
open-webui:
environment:
ENABLE_RAG_WEB_SEARCH: True
RAG_WEB_SEARCH_ENGINE: "searxng"
RAG_WEB_SEARCH_RESULT_COUNT: 3
RAG_WEB_SEARCH_CONCURRENT_REQUESTS: 10
SEARXNG_QUERY_URL: "http://searxng:8080/search?q=<query>"
Create a .env file for SearXNG:
# SearXNG
SEARXNG_HOSTNAME=localhost:8080/
Next, add the following to SearXNG's docker-compose.yaml file:
services:
searxng:
container_name: searxng
image: searxng/searxng:latest
ports:
- "8080:8080"
volumes:
- ./searxng:/etc/searxng:rw
env_file:
- .env
restart: unless-stopped
cap_drop:
- ALL
cap_add:
- CHOWN
- SETGID
- SETUID
- DAC_OVERRIDE
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "1m"
max-file: "1"
Your stack is ready to be launched with:
docker compose up -d
On the first run, you must remove cap_drop: - ALL from the docker-compose.yaml file for the searxng service to successfully create /etc/searxng/uwsgi.ini. This is necessary because the cap_drop: - ALL directive removes all capabilities, including those required for the creation of the uwsgi.ini file. After the first run, you should re-add cap_drop: - ALL to the docker-compose.yaml file for security reasons.
Configure SearXNG for Open WebUI Integration
After starting the container, you need to configure SearXNG to support JSON format queries from Open WebUI:
- Stop the container after about 30 seconds to allow initial configuration files to be generated:
docker compose down
- Navigate to the
./searxngfolder and edit thesettings.ymlfile:
cd searxng
- Open the
settings.ymlfile in your preferred text editor and locate thesearchsection. Addjsonto the formats list:
search:
safe_search: 0
autocomplete: ""
default_lang: ""
formats:
- html
- json # Add this line to enable JSON format support for Open WebUI
Alternatively, you can use the following command to automatically add JSON support:
sed -i '/formats:/,/]/s/html/html\n - json/' searxng/settings.yml
- Save the file and restart the container:
docker compose up -d
Without adding JSON format support, SearXNG will block queries from Open WebUI and you'll encounter 403 Client Error: Forbidden errors in your Open WebUI logs.
Alternatively, you can run SearXNG directly using docker run:
docker run --name searxng --env-file .env -v ./searxng:/etc/searxng:rw -p 8080:8080 --restart unless-stopped --cap-drop ALL --cap-add CHOWN --cap-add SETGID --cap-add SETUID --cap-add DAC_OVERRIDE --log-driver json-file --log-opt max-size=1m --log-opt max-file=1 searxng/searxng:latest
3. Confirm Connectivity
Confirm connectivity to SearXNG from your Open WebUI container instance in your command line interface:
docker exec -it open-webui curl http://host.docker.internal:8080/search?q=this+is+a+test+query&format=json
4. GUI Configuration
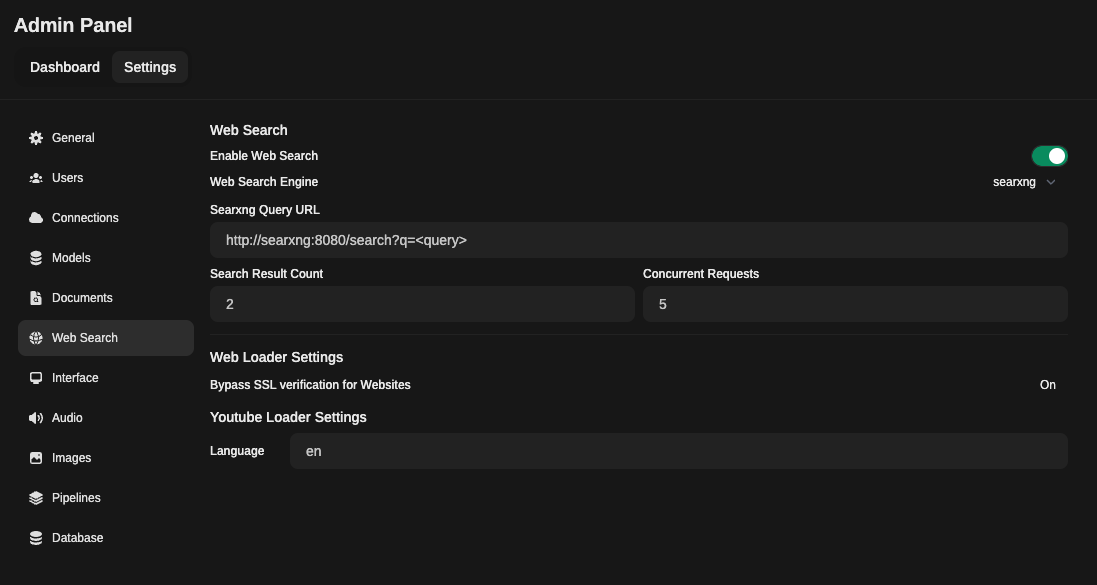
- Navigate to:
Admin Panel->Settings->Web Search - Toggle
Enable Web Search - Set
Web Search Enginefrom dropdown menu tosearxng - Set
Searxng Query URLto one of the following examples:
http://searxng:8080/search?q=<query>(using the container name and exposed port, suitable for Docker-based setups)http://host.docker.internal:8080/search?q=<query>(using thehost.docker.internalDNS name and the host port, suitable for Docker-based setups)http://<searxng.local>/search?q=<query>(using a local domain name, suitable for local network access)https://<search.domain.com>/search?q=<query>(using a custom domain name for a self-hosted SearXNG instance, suitable for public or private access)
Do note the /search?q=<query> part is mandatory.
- Adjust the
Search Result CountandConcurrent Requestsvalues accordingly - Save changes
5. Using Web Search in a Chat
To access Web Search, Click on the + next to the message input field.
Here you can toggle Web Search On/Off.
By following these steps, you will have successfully set up SearXNG with Open WebUI, enabling you to perform web searches using the SearXNG engine.
Note
You will have to explicitly toggle this On/Off in a chat.
This is enabled on a per session basis eg. reloading the page, changing to another chat will toggle off.