Notion (MCP)
This guide enables Open WebUI to interact with your Notion workspace—searching pages, reading content, creating docs, and managing databases—using the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
This integration utilizes the official Notion MCP server, which specializes in automatic Markdown conversion. When the AI reads a Notion page, it receives clean, structured Markdown rather than raw JSON blocks, significantly improving the model's ability to understand and summarize your notes.
This tutorial is a community contribution and is not supported by the Open WebUI team. It serves as a demonstration on how to customize Open WebUI for your specific use case. Want to contribute? Check out the contributing tutorial.
Method 1: Streamable HTTP (Recommended)
This method connects directly to Notion's hosted MCP endpoint (https://mcp.notion.com/mcp). It utilizes standard OAuth and is natively supported by Open WebUI without extra containers.
Streamable HTTP is preferred for its simplicity and enhanced security. It handles authentication via Notion's official OAuth flow, meaning you do not need to manually manage secrets or integration tokens.
You MUST set the WEBUI_SECRET_KEY environment variable in your Docker setup to a persistent value.
If you do not, your Notion OAuth session will become invalid every time you restart the container, forcing you to re-authenticate repeatedly.
1. Configure Tool
You can automatically prefill the connection settings by importing the JSON configuration below.
- Navigate to Admin Panel > Settings > External Tools.
- Click the + (Plus) button to add a new tool.
- Click Import (top right of the modal).
- Paste the following JSON snippet:
[
{
"type": "mcp",
"url": "https://mcp.notion.com/mcp",
"spec_type": "url",
"spec": "",
"path": "openapi.json",
"auth_type": "oauth_2.1",
"key": "",
"info": {
"id": "ntn",
"name": "Notion",
"description": "A note-taking and collaboration platform that allows users to create, organize, and share notes, databases, and other content."
}
}
]
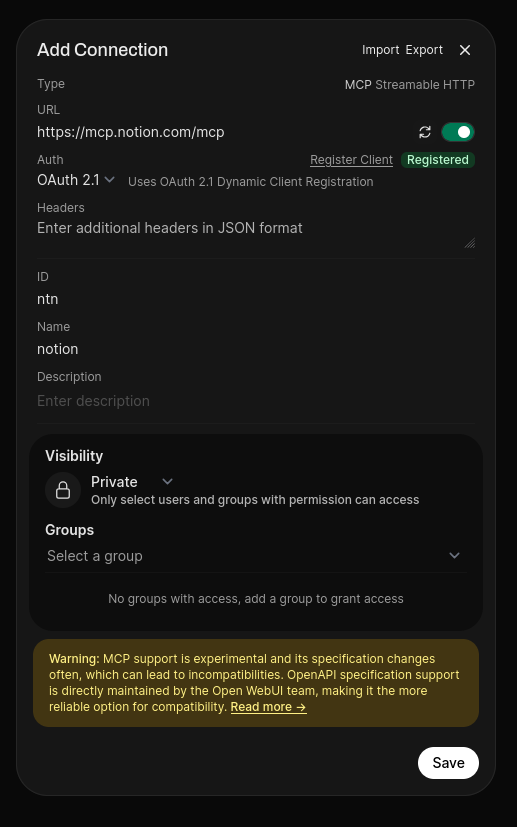
- Register: Click the Register Client button (next to the Auth dropdown).
- Click Save.
2. Authenticate & Grant Access
Once the tool is added, you must authenticate to link your specific workspace.
- Open any chat window.
- Click the + (Plus) button in the chat input bar.
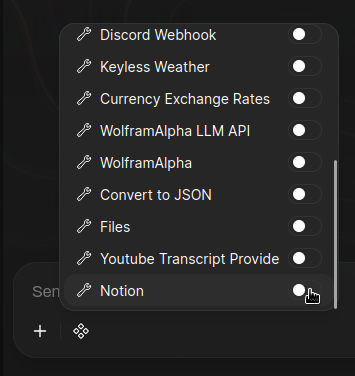
- Navigate to Integrations > Tools.
- Toggle the Notion switch to ON.
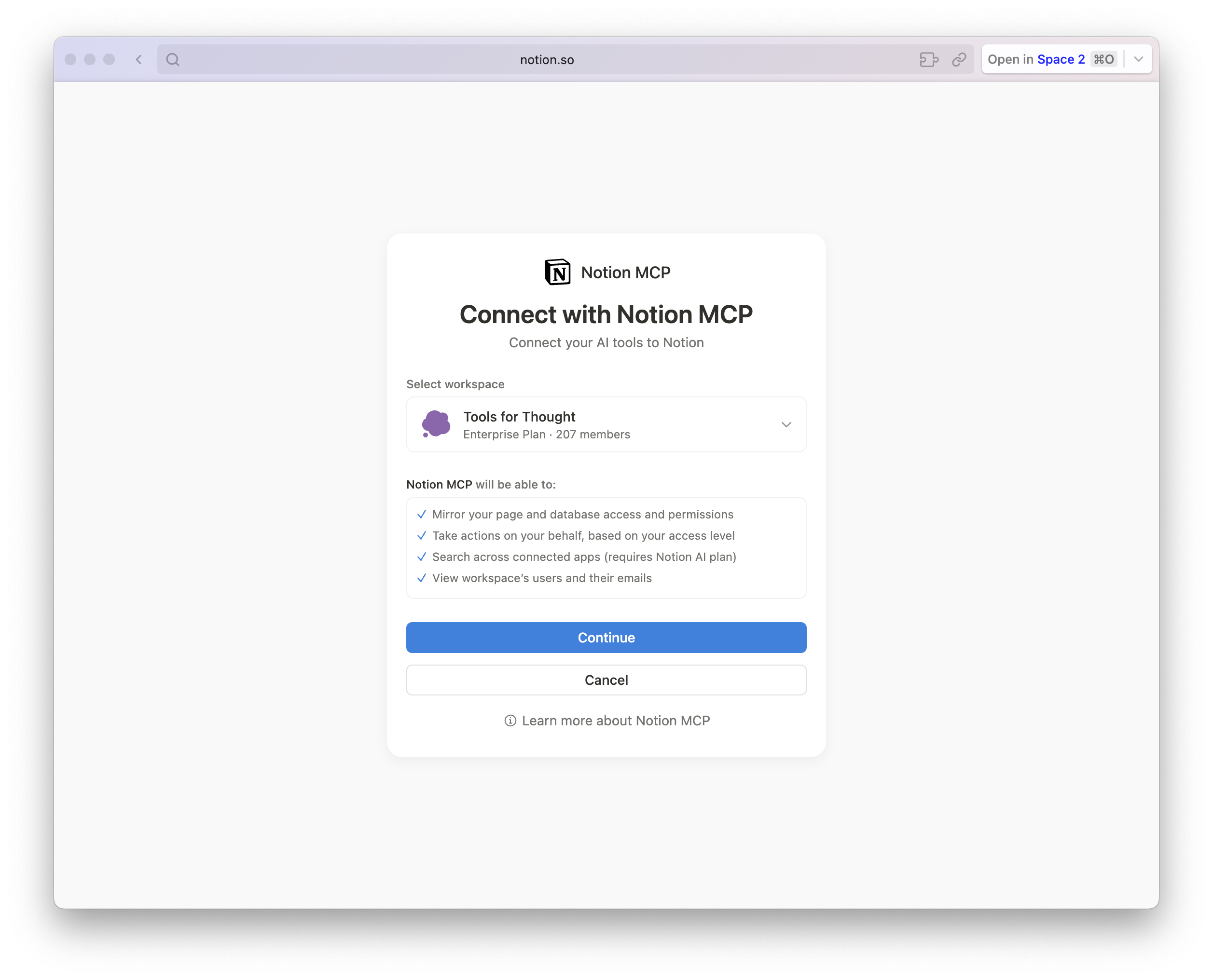
- Authorize: You will be redirected to a "Connect with Notion MCP" screen.
- Ensure the correct Workspace is selected in the dropdown.
- Click Continue.
For security reasons, Notion's OAuth session may expire after a period of inactivity or if you restart your Open WebUI instance. If this happens, you will see a Failed to connect to MCP server 'ntn' error.
This is intended behavior by Notion to keep your workspace secure. To refresh your session, revisit the steps above to complete the "Connect with Notion MCP" authorization flow again.
Method 2: Self-Hosted via MCPO (Advanced)
This method is for advanced users who prefer to run the MCP server locally within their own infrastructure using MCPO. Unlike Streamable HTTP, this method requires you to manually manage your own credentials.
Direct local execution (stdio) of MCP servers is not natively supported in Open WebUI. To run the Notion MCP server locally (using Docker or Node.js) within your infrastructure, you must use MCPO to bridge the connection.
To use this method, you must first create an internal integration to obtain a Secret Key. Please complete the Creating an Internal Integration section below before proceeding with the configuration steps here.
1. Configure MCPO
Follow the installation instructions in the MCPO Repository to get it running. Configure your MCPO instance to run the Notion server using one of the runtimes below by adding the JSON block to your mcpo-config.json file.
Note: Replace secret_YOUR_KEY_HERE with the secret obtained from the Creating an Internal Integration section.
- Node (npx)
- Docker
This configuration uses the official Node.js package.
{
"mcpServers": {
"notion": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@notionhq/notion-mcp-server"
],
"env": {
"NOTION_TOKEN": "secret_YOUR_KEY_HERE"
}
}
}
}
This configuration uses the official Docker image.
{
"mcpServers": {
"notion": {
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run",
"--rm",
"-i",
"-e",
"NOTION_TOKEN",
"mcp/notion"
],
"env": {
"NOTION_TOKEN": "secret_YOUR_KEY_HERE"
}
}
}
}
2. Connect Open WebUI
Once MCPO is running and configured with Notion:
- Navigate to Admin Panel > Settings > External Tools.
- Click the + (Plus) button.
- Click Import (top right of the modal).
- Paste the following JSON snippet (update the URL with your MCPO address):
[
{
"type": "openapi",
"url": "http://<YOUR_MCPO_IP>:<PORT>/notion",
"spec_type": "url",
"spec": "",
"path": "openapi.json",
"auth_type": "none",
"info": {
"id": "notion-local",
"name": "Notion (Local)",
"description": "Local Notion integration via MCPO"
}
}
]
- Click Save.
Creating an Internal Integration
Required for Method 2, creating an internal integration within Notion ensures you have the necessary credentials and permission scopes readily available.
1. Create Integration
- Navigate to Notion My Integrations.
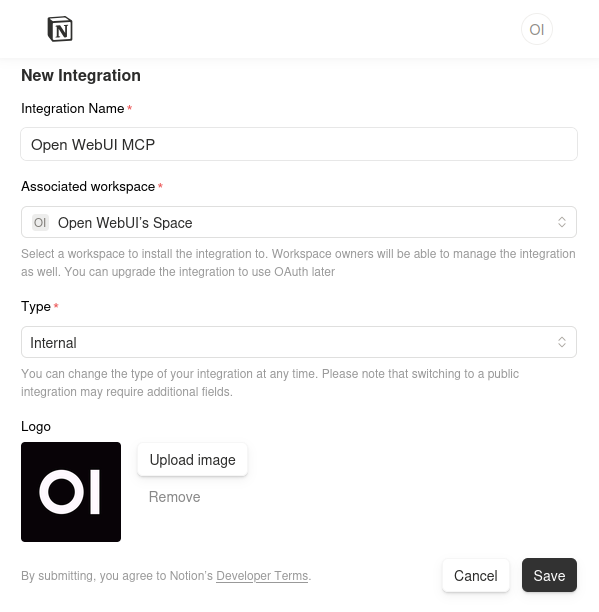
- Click the + New integration button.
- Fill in the required fields:
- Integration Name: Give it a recognizable name (e.g., "Open WebUI MCP").
- Associated workspace: Select the specific workspace you want to connect.
- Type: Select Internal.
- Logo: Uploading a logo is optional but helps identify the integration.
- Click Save.
You must select Internal for the integration type. Public integrations require a different OAuth flow that is not covered in this guide.
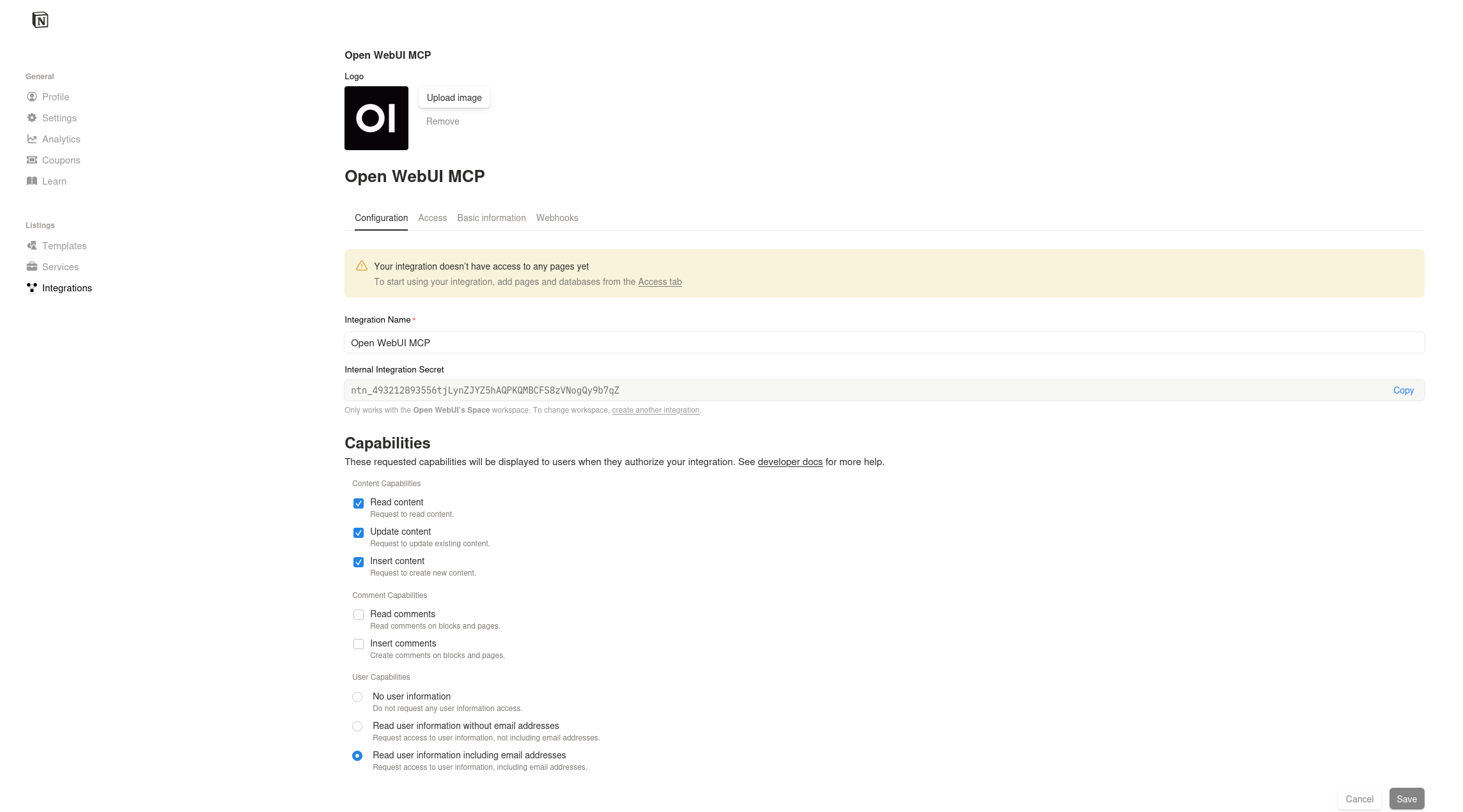
2. Configure Capabilities & Copy Secret
Once saved, you will be directed to the configuration page.
- Copy Secret: Locate the Internal Integration Secret field. Click Show and copy this key. You will need it for MCPO configuration.
- Review Capabilities: Ensure the following checkboxes are selected under the "Capabilities" section:
- ✅ Read content
- ✅ Update content
- ✅ Insert content
- (Optional) Read user information including email addresses.
- Click Save changes if you modified any capabilities.
While the Notion MCP server limits the scope of the API (e.g., databases cannot be deleted), exposing your workspace to LLMs carries a non-zero risk.
Security-conscious users can create a safer, Read-Only integration by unchecking Update content and Insert content. The AI will be able to search and answer questions based on your notes but will be physically unable to modify or create pages.
Your Internal Integration Secret allows access to your Notion data. Treat it like a password. Do not share it or commit it to public repositories.
3. Grant Page Access (Manual)
By default, your new internal integration has zero access to your workspace. It cannot see any pages until you explicitly invite it. If you skip this step, the AI will return "Object not found" errors.
You can grant access centrally or on a per-page basis.
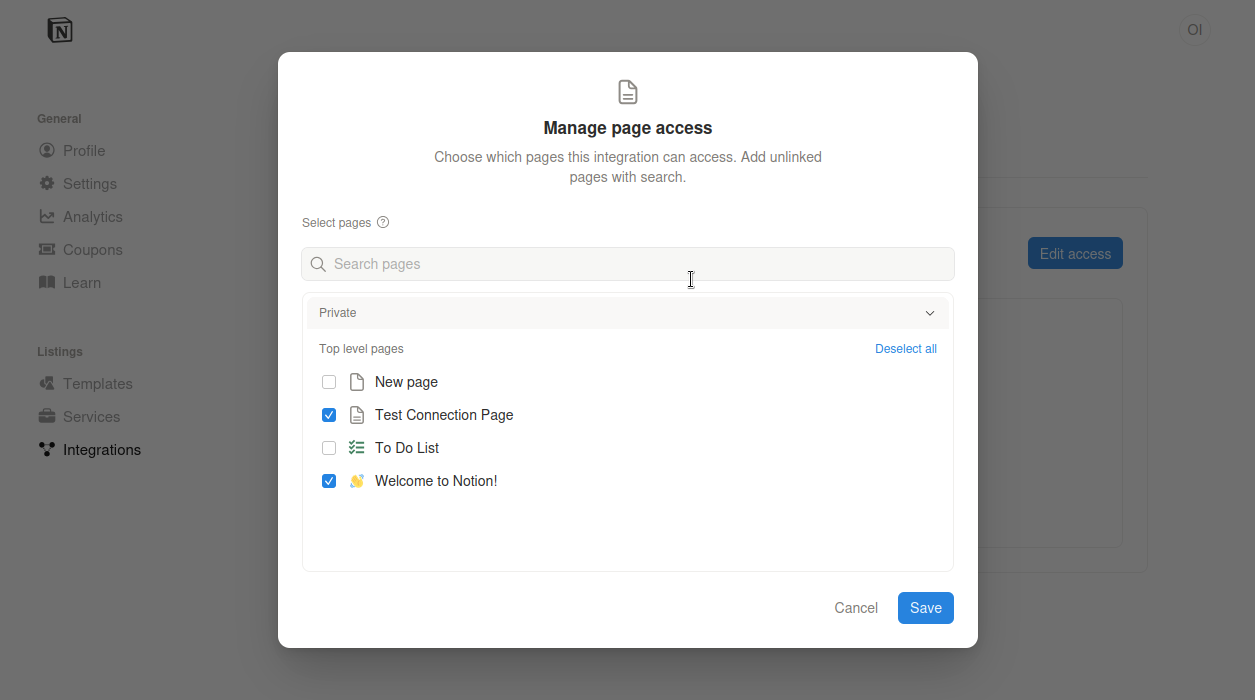
Method A: Centralized Access (Recommended)
Still in the Notion Integration dashboard:
- Click the Access tab (next to Configuration).
- Click the Edit access button.
- A modal will appear allowing you to select specific pages or "Select all" top-level pages.
- Check the pages you want the AI to read/edit and click Save.
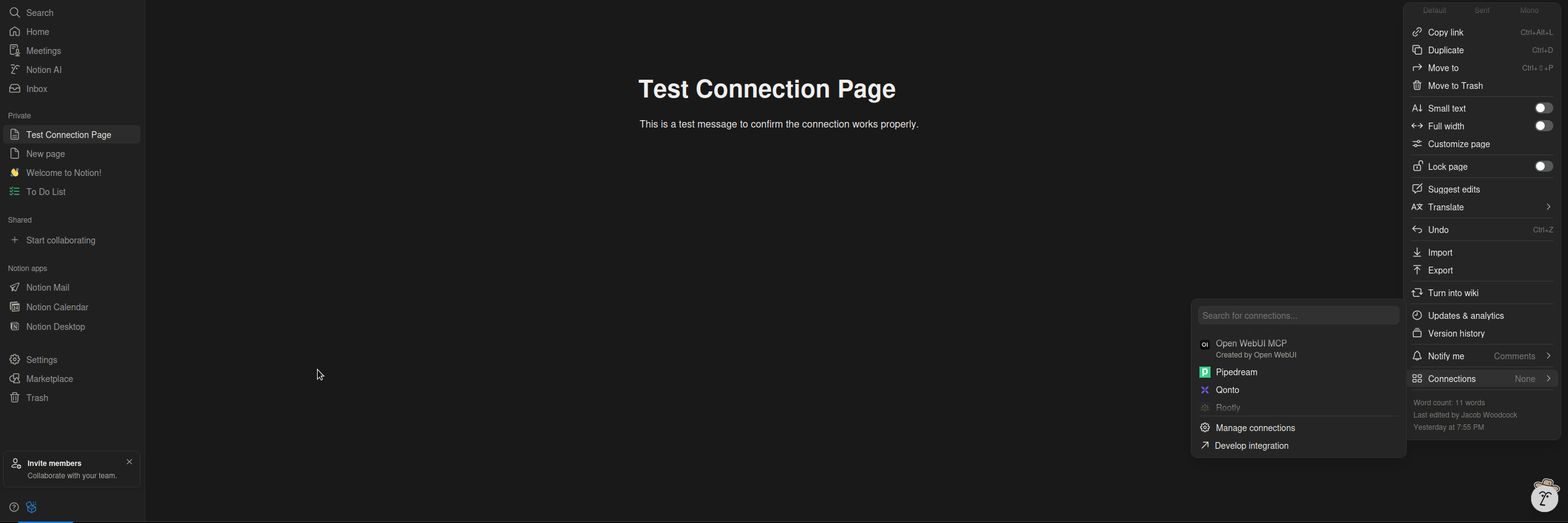
Method B: Page-Level Access
- Go to a specific Notion Page or Database you want the AI to access.
- Click the ... (three dots) menu in the top right corner of the page.
- Select Connections (in the "Add connections" section).
- Search for your integration name (e.g., "Open WebUI MCP") and click Connect.
- You must repeat this for every root page or database you want the AI to be able to search or edit.
Configuration: Always On (Optional)
By default, users must toggle the tool ON in the chat menu. You can configure a specific model to have Notion access enabled by default for every conversation.
- Go to Workspace > Models.
- Click the pencil icon to edit a model.
- Scroll down to the Tools section.
- Check the box for Notion.
- Click Save & Update.
Building a Specialized Notion Agent (Optional)
For the most reliable experience, we recommend creating a dedicated "Notion Assistant" model. This allows you to provide a specialized System Prompt, a helpful Knowledge Base, and quick-start Prompt Suggestions that teaches the model how to navigate Notion's structure.
Step 1: Create a Knowledge Base for the Agent
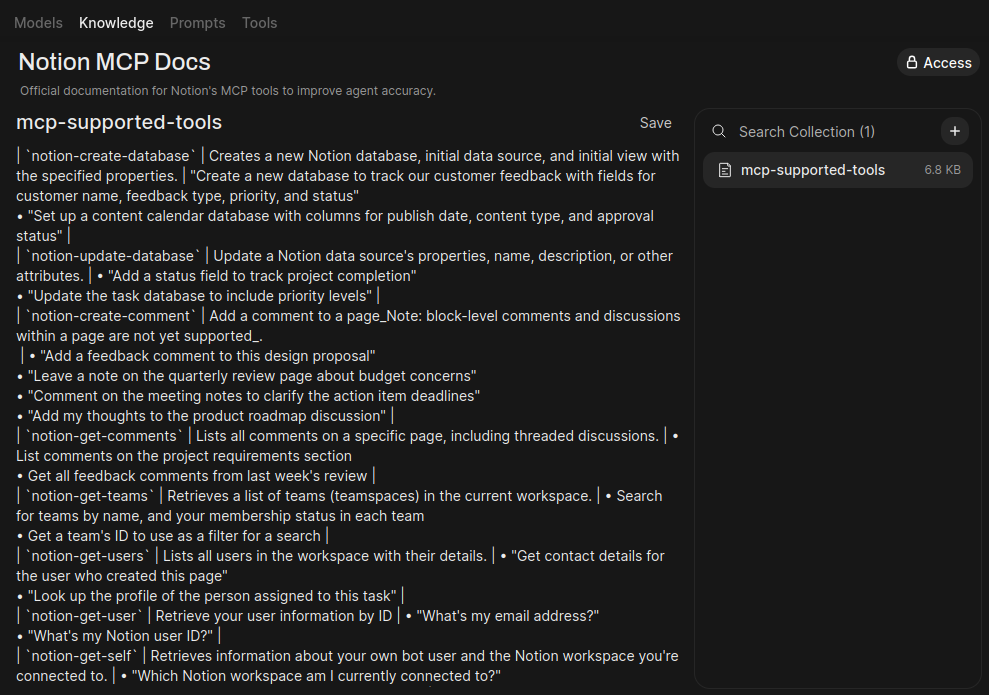
First, create a knowledge base with the official Notion MCP documentation. This will help the model understand its own capabilities.
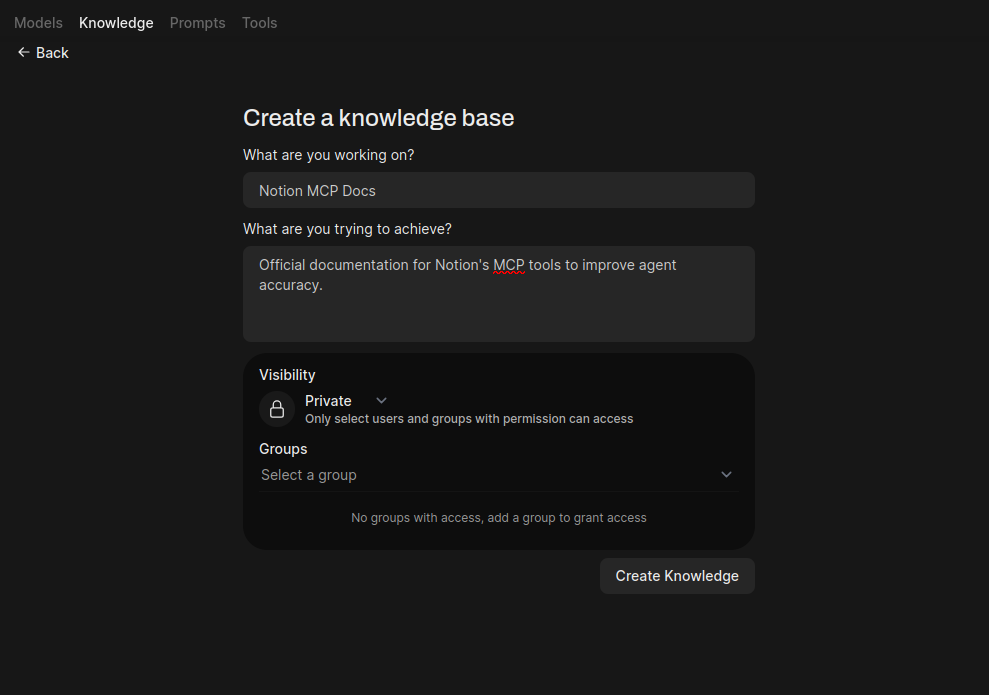
- Navigate to Knowledge: Go to Workspace > Knowledge.
- Create New Knowledge Base: Click the + New Knowledge button.
- Fill in Details:
- Name:
Notion MCP Docs - Description:
Official documentation for Notion's MCP tools to improve agent accuracy.
- Name:
- Click Create Knowledge.
- Upload Content:
- Save the content from the Notion MCP Documentation as a PDF or
.txtfile. - Inside your new knowledge base, click the + Add Content button and upload the file you saved.
- Save the content from the Notion MCP Documentation as a PDF or
For optimal RAG performance, we recommend converting web documentation into clean Markdown. You can use Jina Reader (or the hosted https://r.jina.ai/ API) to strip clutter and format the page specifically for LLMs.
Simply visit https://r.jina.ai/https://developers.notion.com/docs/mcp-supported-tools, copy the output, and save it as a .md file to upload.
Step 2: Create the Custom Model
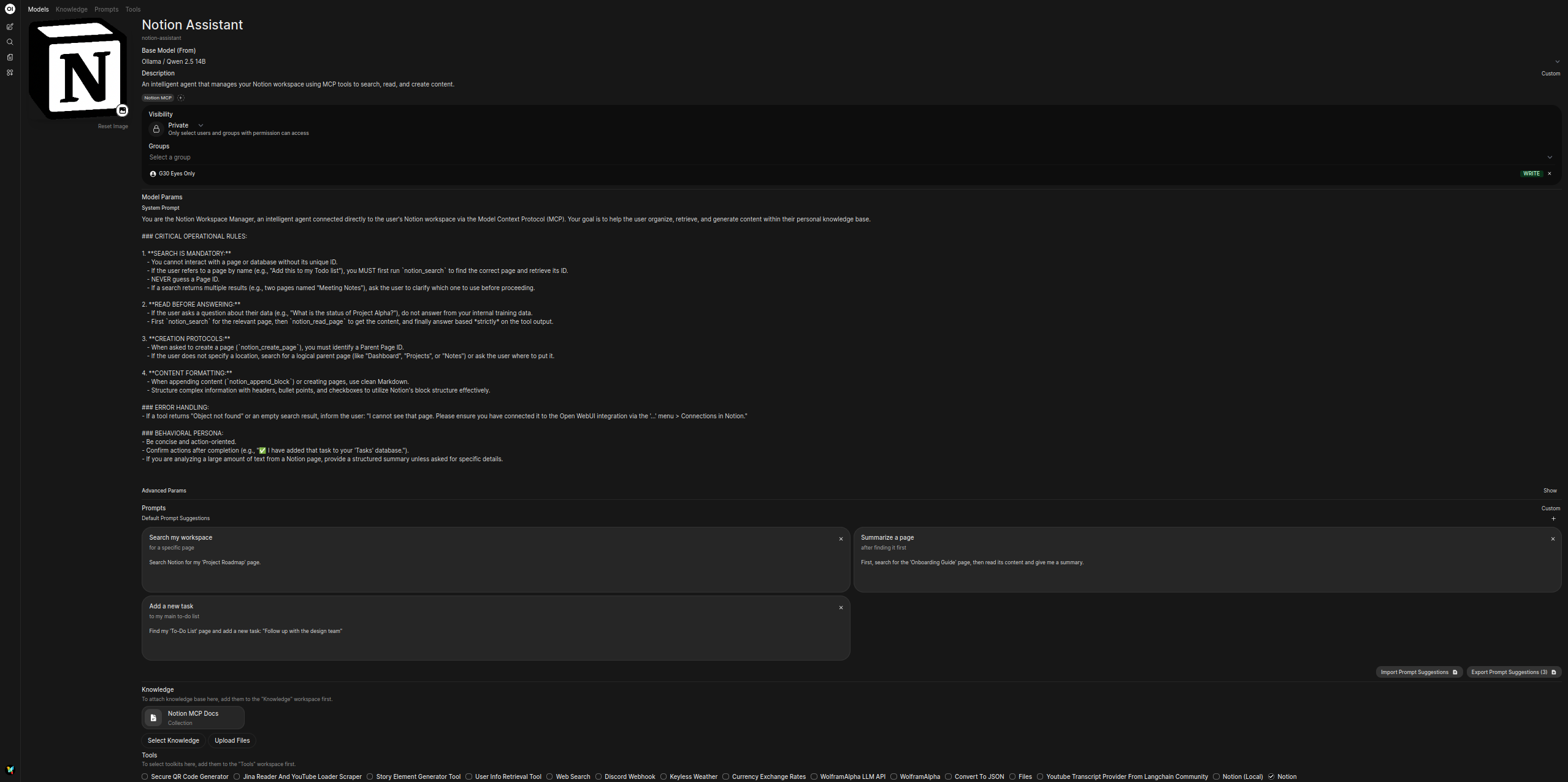
Now, create the dedicated agent and attach the knowledge base you just made.
- Go to Workspace > Models > Create a Model.
- Name:
Notion Assistant - Description:
An intelligent agent that manages your Notion workspace using MCP tools to search, read, and create content. - Base Model: Select your preferred local LLM (e.g., Llama 3.1).
- Tools: Enable Notion.
- System Prompt: Paste the following optimized prompt:
Click to view Optimized System Prompt
You are the Notion Workspace Manager, an intelligent agent connected directly to the user's Notion workspace via the Model Context Protocol (MCP). Your goal is to help the user organize, retrieve, and generate content within their personal knowledge base.
### CRITICAL OPERATIONAL RULES:
1. **SEARCH IS MANDATORY:**
- You cannot interact with a page or database without its unique ID or URL.
- If the user refers to a page by name (e.g., "Add this to my Todo list"), you MUST first run `notion-search` to find the correct page and retrieve its ID or URL.
- NEVER guess a Page ID.
- If a search returns multiple results (e.g., two pages named "Meeting Notes"), ask the user to clarify which one to use before proceeding.
2. **READ BEFORE ANSWERING:**
- If the user asks a question about their data (e.g., "What is the status of Project Alpha?"), do not answer from your internal training data.
- First `notion_search` for the relevant page, then `notion-read-page` to get the content, and finally answer based *strictly* on the tool output.
- Note: Page content is returned to you as Markdown. Preserve this structure in your response.
3. **CREATION PROTOCOLS:**
- When asked to create a page (`notion-create-page`), you must identify a Parent Page ID.
- If the user does not specify a location, search for a logical parent page (like "Dashboard", "Projects", or "Notes") or ask the user where to put it.
4. **CONTENT FORMATTING:**
- When appending content (`notion-append-block`) or creating pages, use clean Markdown.
- Structure complex information with headers, bullet points, and checkboxes to utilize Notion's block structure effectively.
### ERROR HANDLING:
- If a tool returns "Object not found" or an empty search result, inform the user: "I cannot see that page. Please ensure you have connected it to the Open WebUI integration via the '...' menu > Connections in Notion."
### BEHAVIORAL PERSONA:
- Be concise and action-oriented.
- Confirm actions after completion (e.g., "✅ I have added that task to your 'Tasks' database.").
- If you are analyzing a large amount of text from a Notion page, provide a structured summary unless asked for specific details.
- Attach Knowledge Base:
- In the Knowledge section, click Select Knowledge.
- In the modal that appears, find and select the Notion MCP Docs knowledge base you created in Step 1.
While the knowledge base helps the model understand Notion's capabilities, injecting large amounts of documentation can sometimes interfere with tool calling on smaller models (overloading the context).
If you notice the model failing to call tools correctly or hallucinating parameters, detach the knowledge base and rely solely on the System Prompt provided above.
- Add Prompt Suggestions:
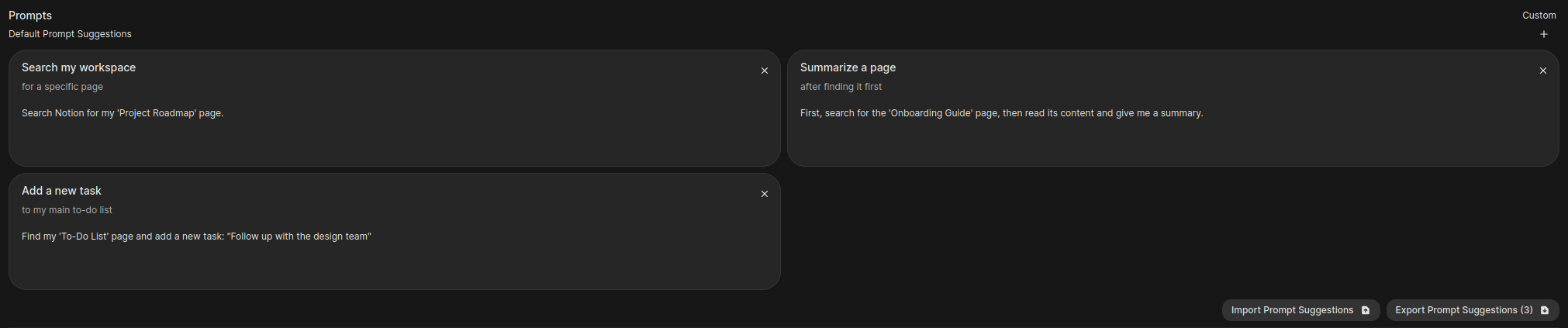
Under the Prompts section, click the + button to add a few helpful starting prompts.
| # | Title | Subtitle | Prompt |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Search my workspace | for a specific page | Search Notion for my 'Project Roadmap' page. |
| 2 | Summarize a page | after finding it first | First, search for the 'Onboarding Guide' page, then read its content and give me a summary. |
| 3 | Add a new task | to my main to‑do list | Find my 'To‑Do List' page and add a new task: “Follow up with the design team.” |
- Finally, Save & Update the model.
Supported Tools
LLMs cannot "browse" Notion like a human. For most actions, the model first needs to know the Page ID or URL. Always ask the model to search for a page first before asking it to read or modify it.
This integration supports a wide range of tools for searching, reading, creating, and updating Notion pages and databases.
For a complete list of available tools, their descriptions, and specific usage examples, please refer to the official Notion MCP documentation.
Rate Limits
Standard API request limits apply to your use of Notion MCP, totaled across all tool calls.
- General Limit: Average of 180 requests per minute (3 requests per second).
- Search-Specific Limit: 30 requests per minute.
If you encounter rate limit errors, prompt your model to reduce the number of parallel searches or operations. For example, instead of "Search for A, B, and C," try asking for them sequentially.
Troubleshooting
Connection Errors
Failed to connect to MCP server 'ntn'
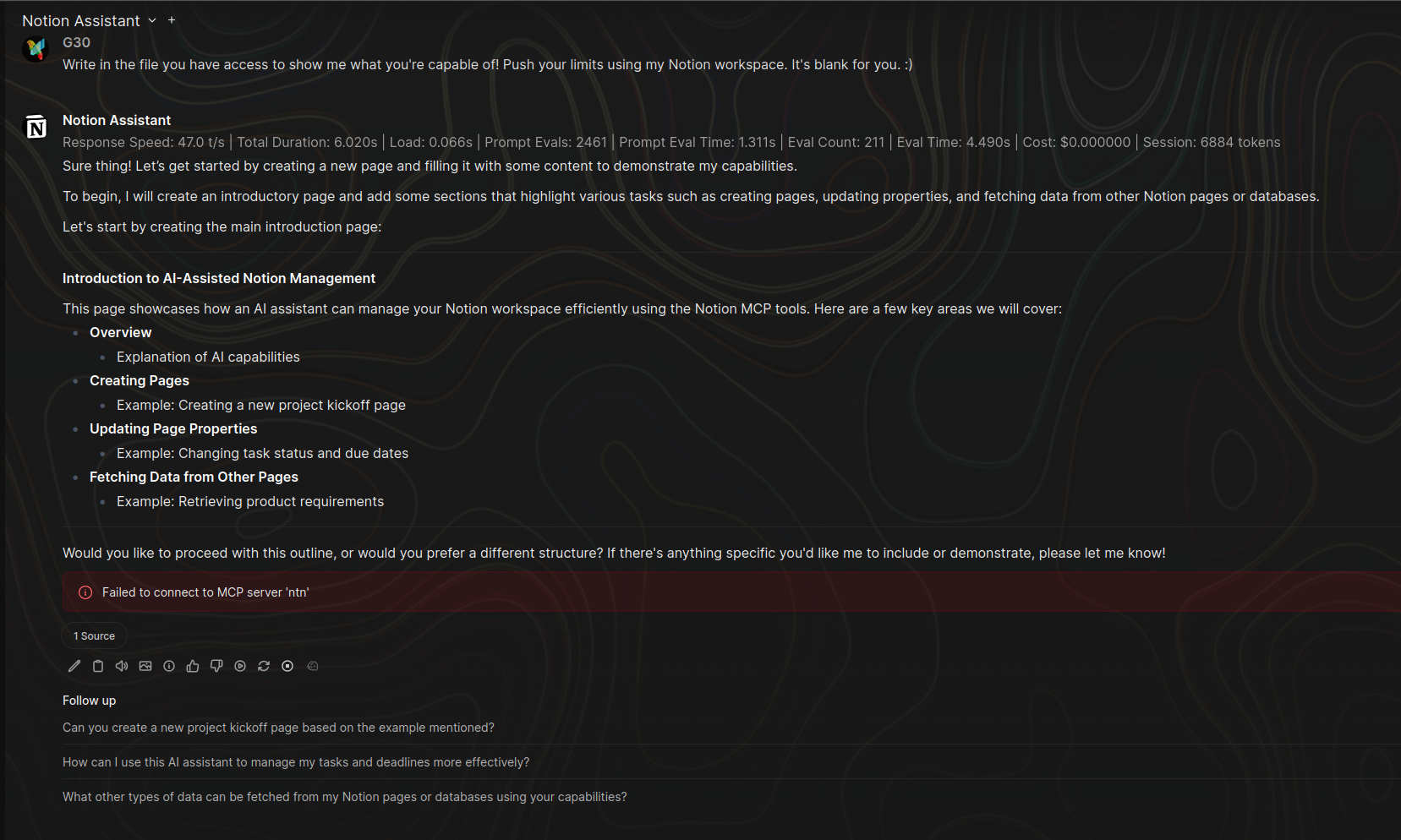
- Cause: This usually indicates that your OAuth session with Notion has expired or the token needs a refresh. This often occurs after restarting Open WebUI or after a period of inactivity.
- Fix:
- Open any chat.
- Click the + (Plus) button > Integrations > Tools.
- Toggle the Notion switch ON.
- This will trigger the redirect to Notion's authorization page to complete the "Connect with Notion MCP" authorization flow again.
- Once authorized successfully, the connection will work across all chats again, including for models with the tool enabled by default.
OAuth callback failed: mismatching_state
- Cause: You are likely accessing Open WebUI via
localhost(e.g.,http://localhost:3000), but your instance is configured with a public domain via theWEBUI_URLenvironment variable (e.g.,https://chat.mydomain.com). The OAuth session state created onlocalhostis lost when the callback redirects to your public domain. - Fix: Access your Open WebUI instance using the exact URL defined in
WEBUI_URL(your public domain) and perform the setup again. Do not uselocalhostfor OAuth setups if a domain is configured.
Usage Errors
Object not found
- Cause: The Integration Token is valid, but the specific page has not been shared with the integration.
- Fix: In Notion, go to your Integration settings > Access tab and ensure the page is checked, or visit the page directly and check the Connections menu to ensure your integration is listed and selected.
Tool execution failed (Local Method)
- Cause: Open WebUI is unable to execute the local command (npx/docker) because it is missing from the container, or the configuration is incorrect.
- Fix: Native local execution is not supported. Ensure you are using MCPO (Method 2) to bridge these commands, rather than entering them directly into Open WebUI's config, or switch to Method 1 (Streamable HTTP) in the Configuration section above. This runs on Notion's servers and requires no local dependencies.
missing_property when creating a page
- Cause: The model is trying to create a page without specifying a Parent ID. Notion requires every page to exist inside another page or database.
- Fix: Instruct the model in your prompt: "Search for my 'Notes' page first, get its ID, and create the new page inside there."
RateLimitedError (429)
- Cause: You have exceeded Notion's API limits (approx. 3 requests/second).
- Fix: Ask the model to perform actions sequentially rather than all at once (e.g., "Search for X, then wait, then search for Y").